February 2023
It’s important you know the difference between management accounting and financial accounting, says Karen Groves, who is here to help.
As part of your AAT studies, you may get a task in the assessment on financial accounting versus management accounting. So, what is the difference between the two?
Financial accounting
The main purpose of financial accounting is to produce the statutory financial statements for external users. Financial statements are prepared on a regular basis, usually once a year, and are set out in a standard format dictated by law and accounting standards, which includes a statement of financial position and a statement of profit or loss.
The financial statements are a historic record of the organisation’s financial transactions for the period. The users of the financial statements can include:
• HM Revenue and Customs – to work out what tax the business needs to pay.
• Potential future investors – to see how the business is performing and decide on whether to invest or not.
• Business owners – to assess the profitability and business performance.
• Employees – both current and new, to see how the business is performing as this will impact on job security and potential growth opportunities within the job role.
Management accounting
Management accounting describes the process of identifying, measuring, analysing, and interpreting financial information used by managers. This assists with planning, controlling and decision making, and to ensure the appropriate use of, and accountability for its resources.
An example of management accounts could be a quarterly sales report which would be prepared from the sales of the business and analysed between the different sales representatives to establish who had achieved the most sales in the period, or done by region.
Management accounts are produced from the accounting transaction records of the business and may be presented in any format which is useful for the business in making business decisions, as there is no legal requirement. They may be prepared monthly, or quarterly, or whatever the business requires, however they are usually prepared on a monthly basis.
The aims of management accounting are:
Decision making: Management accounts are financial information reports which are usually made available to the internal management of the business to inform and assist the management’s decision-making process, for example, what new product to launch.
Planning: When a business is looking forwards to a new accounting period, they will want to know how much income they might expect from sales and how much cost they expect to incur, for example rent costs.
This information is used to set a budget.
Communicating: Management information can be very helpful when management need to feedback performance information to a range of departments, or to communicate business aims.
Co-ordinating: All departments should be co-ordinated and work together to achieve the business aims.
Motivating: Management accounts will include targets which should be set to motivate managers and their staff and improve performance.
Targets should be realistic and achievable, because if they are too difficult to achieve then they are likely to demotivate staff.
Controlling: Once a budget is set for a future period it is important to then compare what has actually happened, to see if there is any significant over or under spending in comparison to the budget and investigate the cause.
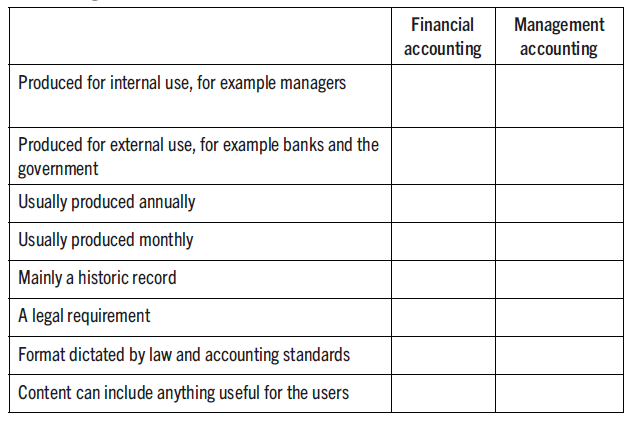
Question
Identify if the statements below apply to financial or management accounting:
Answer
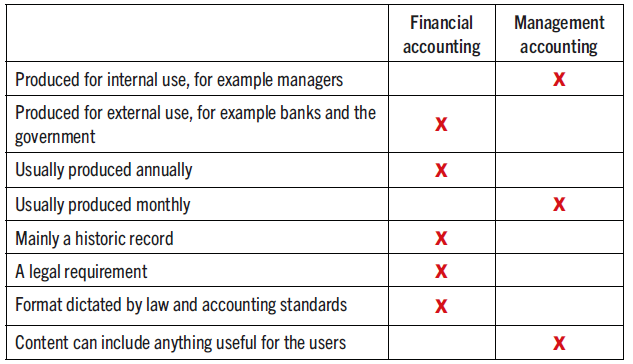
Identify if the statements below apply to financial or management accounting:
• Karen Groves is an AAT tutor and AAT Course Director at e-Careers